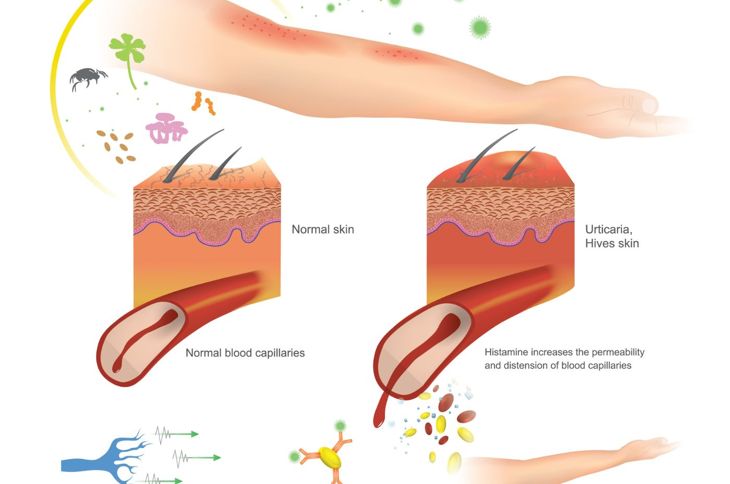
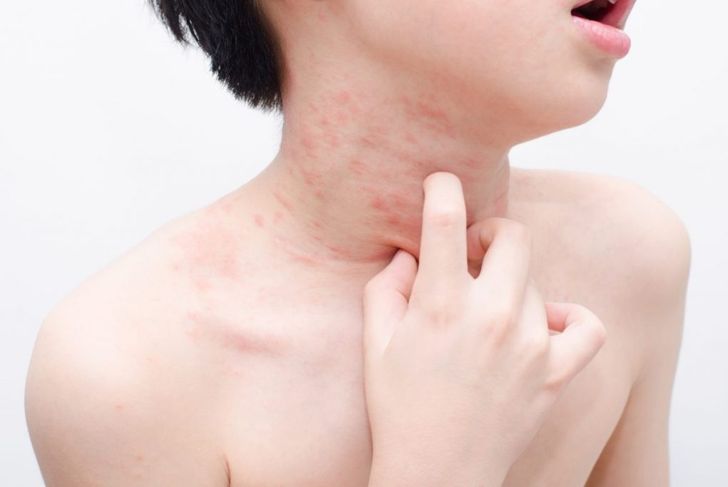
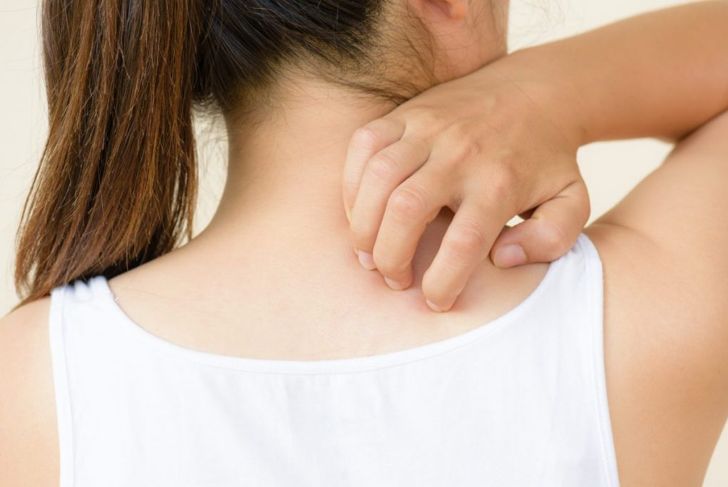
Acute urticaria is hives or other swelling that lasts less than six weeks. Hives occur for many different reasons, and a person with hives may experience itching, redness, or pain. Although symptoms may come on quickly and without explanation, hives are rarely a medical emergency, and at-home treatment is typically effective. Any part of the body can break out in hives including the lips, tongue, ears, and genitals.
What are the most common causes of urticaria?
Urticaria, or hives, most often occur as an allergic reaction, usually to something internal such as food or medication. Hives may also occur as a reaction to a substance or material that has come into contact with the surface of the skin. Common culprits include:
- Milk and other dairy products
- Fish or shellfish
- Strawberries
- Eggs
- Nuts
- Soaps or lotions
- Wool clothing
Hives may also occur as the result of stress, infection, or underlying illness. Treatment is normally quite simple. Determining the cause, however, may not be quite so easy.
When is urticaria considered an emergency?
Urticaria is rarely life-threatening. However, when hives occur inside the throat or lungs or on the tongue, airways may be blocked. When this happens, it is important to seek medical assistance immediately. Generally, these hives occur as an allergic response to something eaten or inhaled. Patients feel as though their throat is closing off and experience difficulty breathing. Breathing difficulty tends to worsen rapidly with each breath, making immediate transport to the hospital vital.
What does urticaria look like?
Urticaria will present as flesh-toned or pale pink skin bumps. They may be round or asymmetrical in shape. The bumps can vary in size and can cover the entire body or be localized to a small area, depending on the cause. Hives are usually very itchy, and the surrounding area turns a deeper red color if they are scratched or picked. Generally, the surface of the hives themselves will remain relatively pale.
What does urticaria feel like?
To the touch, urticaria feels like patches of raised or swollen skin. The hives themselves are smooth, and the skin should be unbroken unless the affected person has scratched excessively. Patients with urticaria will most likely feel severely itchy; in some cases, the hives may also cause a burning or stinging sensation. Other symptoms are rare.
How is urticaria diagnosed?
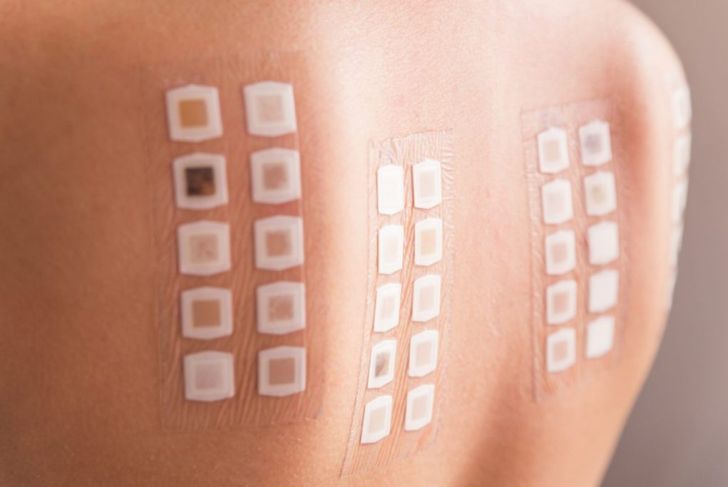
Unfortunately, there is no test available to determine the presence of urticaria. If a patient is experiencing an itchy, bumpy skin rash, a doctor will diagnose based on medical history and other factors. One question the doctor will likely ask is what the patient was doing or eating when the hives appeared. This may aid the doctor in both confirming the diagnosis and confirming the cause. However, it may not always be possible for the doctor to determine the cause of the outbreak. Sometimes, a confirmed diagnosis of urticaria is impossible.
How does a doctor determine the cause of urticaria?
The doctor will investigate the hives physically and ask a series of questions to determine the most likely underlying cause. If an underlying illness or infection is suspected, the doctor will order bloodwork to confirm. If the doctor presumes an allergic reaction caused the hives, skin tests can confirm the presence of allergies. These tests don’t always yield results, but may help the doctor narrow the possibilities.
How is urticaria treated?
A doctor may recommend you treat urticaria with antihistamine medication. Patients who experience frequent breakouts may need to regularly administer antihistamines to prevent recurring reactions. Calamine lotion can be used to topically treat itching caused by hives, while over the counter pain relievers are usually enough to help with any pain. In severe cases, a doctor may administer injectable medications to combat the outbreak more effectively and quickly. These cases are medical emergencies and usually occur when the hives develop in the mouth, throat, or lungs.
Managing urticaria at home.
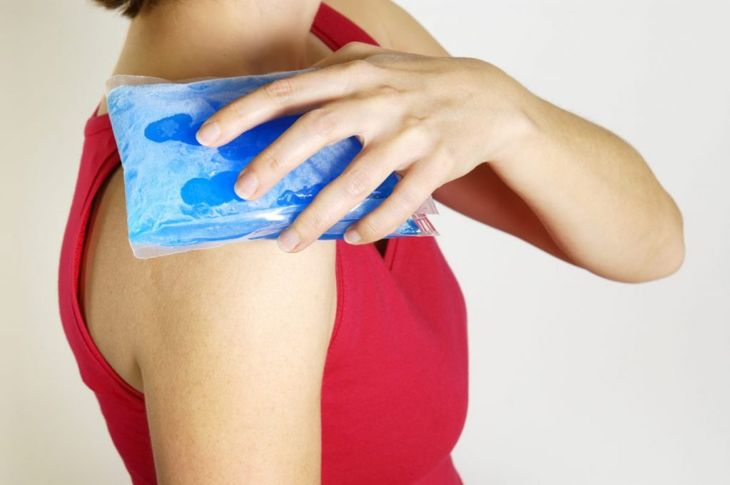
For less severe cases that do not require medication, there are a few things a person with hives can do to relieve discomfort. Using a cool compress on the area can be helpful in relieving itching and minor pain. Keeping the environment at a cool temperature and wearing soft, loose-fitting clothing can be helpful as well.
What other symptoms may accompany urticaria?
Most often, hives appear without any further complications. In rare cases though, other symptoms may present and can be signs of anaphylaxis or other serious conditions. These symptoms include dizziness, shortness of breath, wheezing, and swelling of the lips, tongue, throat, or face. If these symptoms do occur alongside urticaria, consult a doctor immediately.
What underlying conditions may cause urticaria?
Viral and bacterial infections are common causes of urticaria in both children and adults. Culprits include the common cold, influenza, urinary tract infections, and hepatitis, among others. Many other conditions may cause hives to appear, including thyroid disease, lupus, and vasculitis. Some cancers present with hives, and metabolic disorders can lead to occasional outbreaks of urticaria.

 Home
Home Health
Health Diet & Nutrition
Diet & Nutrition Living Well
Living Well More
More