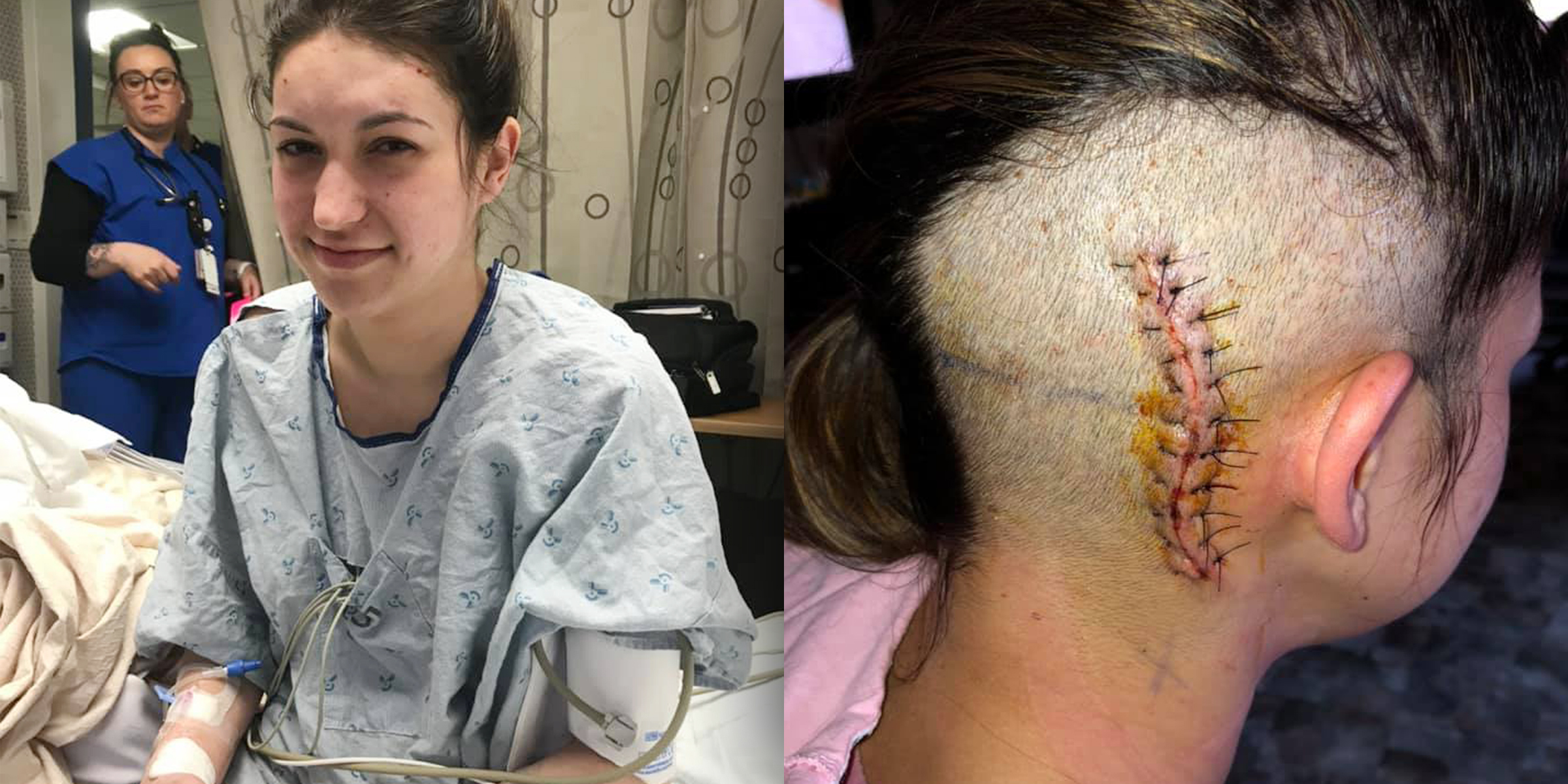
A tumor is an abnormal growth of cells in the body, and can either be benign (not cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Symptoms of a tumor can vary depending on the location, size, and type of tumor.
Common symptoms include:
Pain or discomfort
Swelling or lumps
Fatigue
Unexplained weight loss
Changes in bowel or bladder habits
Skin changes, such as yellowing
Persistent coughing or trouble breathing
Persistent headaches
Diagnosis of a tumor can involve a physical examination, imaging tests (such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI), biopsy, and blood tests.
Treatment for Tumor
Treatment for a tumor depends on several factors, including the type, location, and size of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health. Treatment options may include:
Surgery: The removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue
Radiation therapy: The use of high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells
Chemotherapy: The use of drugs to kill cancer cells
Targeted therapy: The use of drugs that target specific genes or proteins involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells
Immunotherapy: The use of drugs that help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells
In some cases, a combination of treatments may be used. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for an individual case.
Conclusion
Tumors can have a wide range of symptoms and the best treatment option will depend on the specific case. If you have any concerns or suspect you may have a tumor, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider.

 Home
Home Health
Health Diet & Nutrition
Diet & Nutrition Living Well
Living Well More
More