In 1954, four infants from the same family died within their first 90 days of life. Doctors attributed the deaths to a neurodegenerative disorder. All four babies had the same odd symptom: their urine had a burned sugar smell. Maple syrup urine disease, MSUD, is a rare genetic disorder caused by a defect in the breakdown of the amino acids leucine, isoleucine, and valine. Within a few days of birth, a maple syrup odor is detectable in urine and, in some cases, earwax and sweat. If left untreated, MSUD leads to deadly conditions such as neurodegeneration and encephalopathy.
Causes
Researchers discovered that the mutations in BCKDHA, BCKDHB and DBT genes cause the catabolic defect leading to maple syrup urine disease. In addition to the accumulation of those three amino acids, their toxic byproducts or keto acids also build up in the body, causing metabolic acidosis, where the kidneys fail to remove enough of the acids. Studies show that in general, one in 185,000 people has MSUD. Certain ethnic groups have higher occurrences: in the Ashkenazi Jewish population the condition affects one in every 26,000 live births, while in the Mennonite population, the rate is as high as 1 in 380.
Classic MSUD
Though some don’t match the defined protocols, the majority of individuals with MSUD fall into four subtypes. Classic MSUD is apparent within the first few days of birth. The baby does not feed well from the breast or the bottle. Without these nutrients, the child becomes irritable and lethargic. As she disengages, neurological signs such as athetosis, slow and convoluted writhing movements of the digits, limbs, neck and tongue, may develop. This progresses to hypertonia, where muscles become rigid even when at rest. Spasms, convulsions, and coma may also occur, and at a certain point, neurological and respiratory failure are inevitable.
Intermediate MSUD
With intermediate MSUD, symptoms may appear as early as five months to up to seven years. They may experience seizures as well as neurological and developmental impairments as a result of increased enzyme activity. While some may exhibit the maple syrup odor in sweat, urine, and earwax, others may be asymptomatic until later. Because ataxia, the inability to control bodily movements, is also a symptom, the child may be misdiagnosed before the proper diagnosis is reached.
Living with Classic and Intermediate MSUD
Classic MSUD is the most severe form of the disorder, followed by intermediate. While these conditions can be fatal if untreated, even stabilized children have lifelong issues. They may have intellectual limitations that could lead to behavioral issues including ADHD and anxiety. Additionally, they may be prone to osteoporosis due to loss of bone mass. Some develop high blood pressure in the skull that can cause painful headaches.
Intermittent MSUD
Children with intermittent MSUD have normal growth, diet, and intellectual development. At a later stage during a stressful experience or after contracting an infection, the disorder is triggered with symptoms that include the characteristic odor, ataxia, and lethargy. The sudden onset of metabolic crisis may result in brain damage, seizure, or other neurological complications.
Thiamine-Responsive MSUD
In 1971, doctors in Montreal Children’s Hospital gave a female infant with elevated branched-chain amino acids 10 milligrams of thiamine. Her BCAA plasma levels returned to normal. That was the first observed case of thiamine-responsive MSUD. Thiamine or vitamin B1 helps in amino acid metabolism, and this less severe subtype responds well to large dosages of the vitamin. Between 10 and 100 milligrams improve enzyme action, compared to a daily requirement of just 1.1 milligrams for healthy people.
Treatment and Management Objectives
Maple syrup urine disease treatments aim to provide medical nutrition therapy and manage metabolic episodes. The idea is to reduce ketoacidosis through dietary restriction until plasma concentrations are stable. Once that’s achieved, coming up with a plan to maintain and enable development is the long-term goal. Children diagnosed with MSUD need aggressive treatment to help with constructive metabolism. Studies show some retrovirals can infect MSUD lymphocytes and correct the enzyme deficiency.
Diagnostic Options
There are a few ways to diagnose infants with maple syrup urine disease. Tandem mass spectrometry uses a single blood sample to screen for many disorders, including MSUD. When advanced screening is not available, doctors may need to rely on symptomatic findings and test for keto acids through urine and blood analysis. However, infants with intermittent MSUD may have normal results, and that’s where family history and molecular genetic testing would indicate the mutations. The earlier the diagnosis, the more prepared parents and doctors will be.
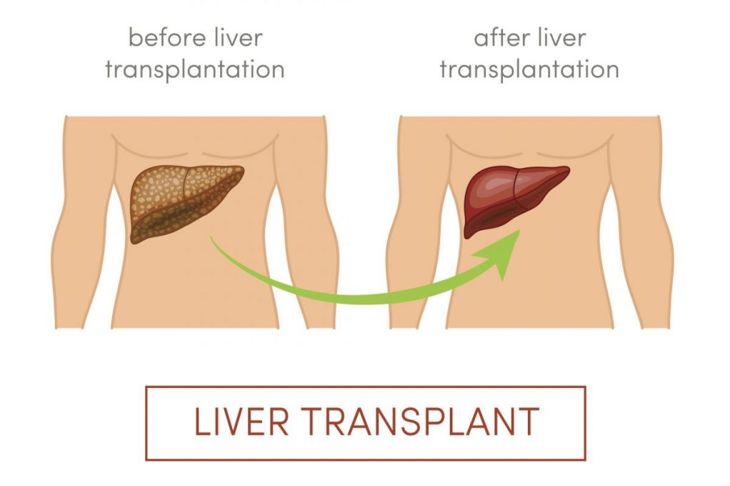
Radical Treatment Option: Liver Transplant
Studies show liver transplants can successfully treat those with classic MSUD. Following the procedure, children could eat protein-rich foods and live symptom-free lives thanks to the new liver’s enzymes. While the research results are promising, more needs to be done as liver transplants are both costly and difficult to procure.
Related Disorders: MMA and PA
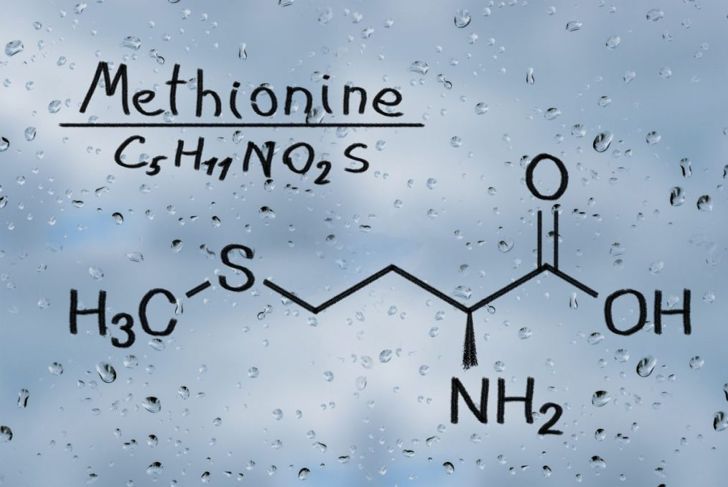
A few related disorders similar to MSUD may help doctors not only diagnose but understand the disorder. Methylmalonic acidemia, MMA, is caused by mutations in five genes that prevent the body from metabolizing methionine, valine, isoleucine, and threonine. Developmental delay and failure to thrive are some initial symptoms. Propionic acidemia, PA, is caused by a deficiency of the propionyl CoA carboxylase enzyme used to break down amino acids. It can result poor nutrition and seizures within the first weeks of birth. Both disorders require dietary restrictions and medication, depending on the severity.

 Home
Home Health
Health Diet & Nutrition
Diet & Nutrition Living Well
Living Well More
More