Meningitis is a severe inflammatory condition that affects the innermost layer of the meninges (the delicate membranes that protect both the brain and the spinal cord), called the arachnoid layer, and the fluid that circulates in the ventricles and the subarachnoid space- the cerebrospinal fluid. It is categorized as a medical emergency. Typically, Meningitis is caused by infections that are transmitted by microorganisms, particularly bacteria and viruses. Anyone can be affected by meningitis. However, children under five years and teenagers are the most at risk of bacterial infection due to meningococcus. In some cases, other diseases can have an impact on the meninges as do certain drugs as well. If meningitis is detected in the early stages, a range of treatments including antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and corticosteroids may be prescribed, based on what is causing the infection. Early detection is of utmost importance. It is then advised that one be vigilant vis-a-vis their health. If symptoms of meningitis happen to manifest, seek immediate medical assistance. These are ten signs to watch out for they may signal the contraction of meningitis.
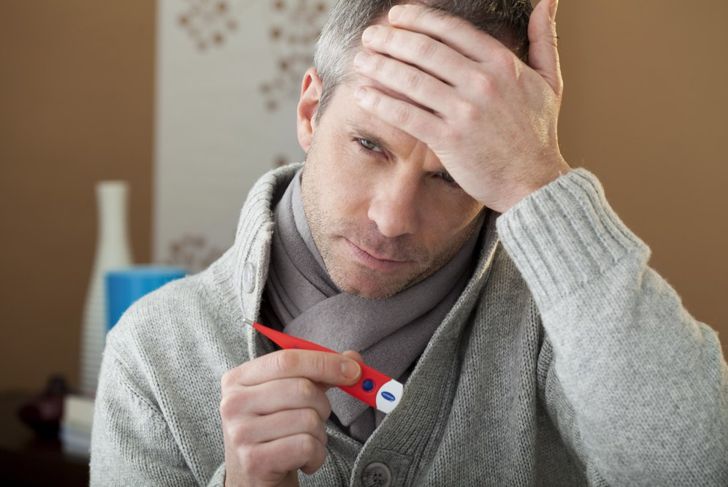
Fever
People with both bacterial and viral meningitis tend to have a temperature. With bacterial meningitis, the fever usually presents itself suddenly, reaching high temperatures that can be anxiety-provoking. This high-temperature patient may experience cold hands or feet. Viral meningitis causes low-grade fever in most instances that easily subsides with over-the-counter medication. The fever in both cases is accompanied by chills as well, often leading people to confuse meningitis with common flu.
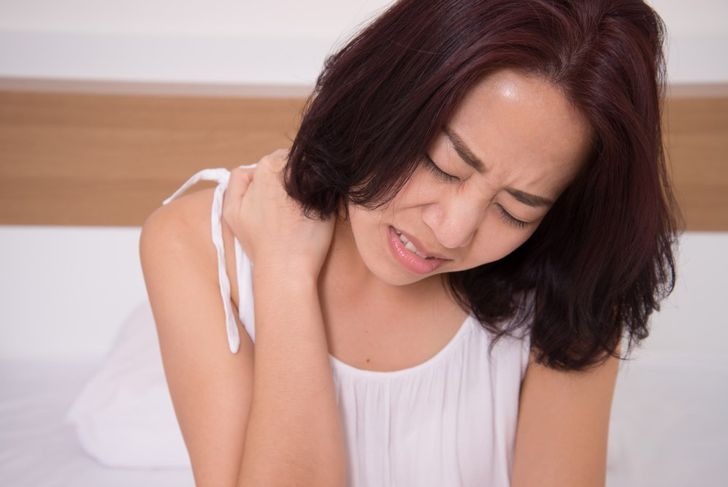
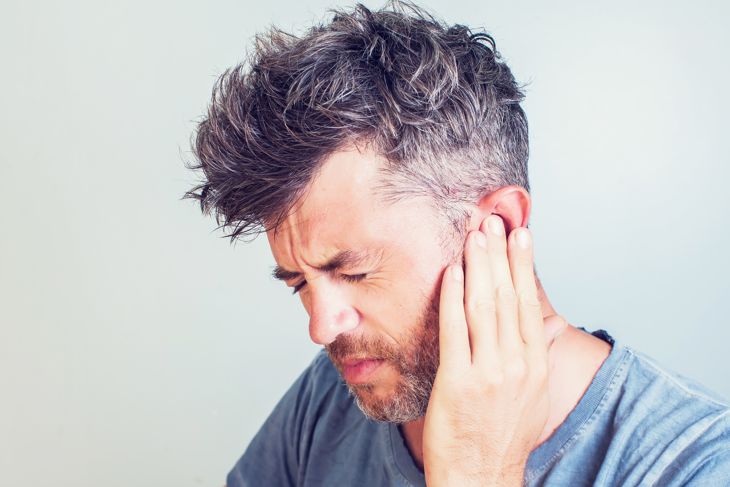
Stiffness in Neck
A classic symptom of meningitis is stiffness in the neck, which prevent passive flexing of the neck. If a meningitis patient suffers from neck stiffness, it implies that the infection has settled in his nervous system, causing inflammation of the membranes in the neck region.
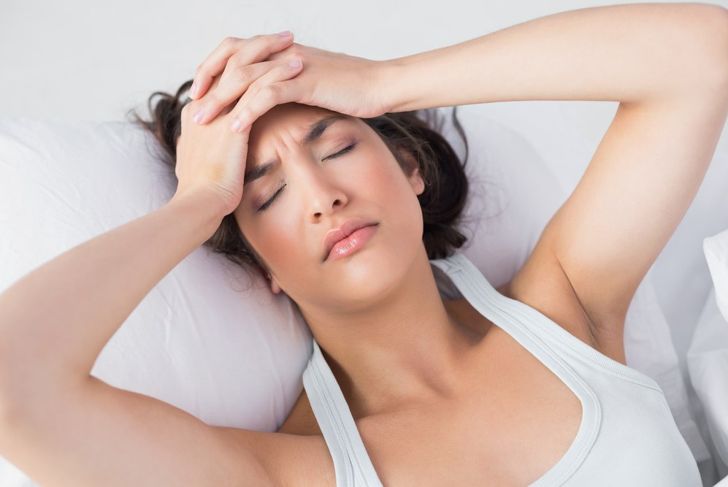
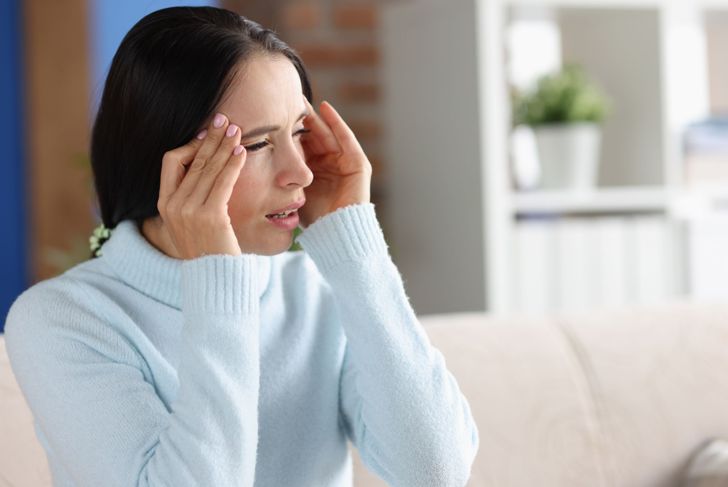
Severe Headaches
Many patients affected by meningitis experience a severe, persistent headaches. It is considered to be extremely intense and easily differentiable from other, ordinary headaches. It is caused when the meninges of the brain get infected and thus inflamed. The brain, held in a non-expansive immovable skull, gets pressurized by the skull when the swelling gets severe. This causes an acute headache, which given the nature of its origin, is different in its manifestation from regular headaches as well.
Nausea and Vomiting
Individuals with meningitis may also find themselves suffering from unprecedented nausea, which may or may not is followed by a vomiting spell. Nausea and vomiting occur when the inflammation of the meninges causes intracranial pressure to rise and stimulates the vomiting center of the brain. The more severe the infection, the more likely it is that the patient’s nausea translates into a vomiting spell.
Photophobia
Photophobia is a term used to denote abnormal intolerance to light that causes discomfort or pain in the eyes. It is a symptom that is commonly associated with meningitis, but a lesser majority of patients tend to suffer from it. Why meningitis causes, this is not fully understood in the medical world though it has been established that meningeal irritation is responsible for it at some level. Regardless of the cause, photophobia can be very traumatizing to patients with meningitis.
Phonophobia
In medical terms, phonophobia suggests an intolerance to sounds, especially those at high frequencies. Like photophobia, phonophobia is also a common symptom observed in meningitis patients; it causes them to feel extremely uncomfortable around loud sounds. This, alongside photophobia, happens to be amongst the more distressing outcomes of meningitis. People suffering from either or both of these symptoms often seclude themselves in dark, quiet places in the hopes of getting some relief.
Lack of Mental Agility
Those suffering from bacterial meningitis are also likely to exhibit a loss of mental agility. They may seem constantly drowsy, often expressing a desire not to wake up and leave the bed. At other times, they may be confused and lost in ordinary situations that would otherwise be easily understood. Extreme irritability in bacterial meningitis patients is also common. It is suggested that an increase in intracranial pressure leads to neuronal damage and depending upon which area of the brain is affected, allied neurological deficits such as those mentioned above occur.
Lack of Appetite
Many meningitis patients, especially children, exhibit disinterest in food consumption during their illness and while recovering as well. The exact cause of this loss of appetite in meningitis is not yet established even though it is a widely prevalent symptom of this condition. Some experts suggest that it is merely the trauma of physical suffering that leads patients to reject food. However, there is little consensus over this, and thus, loss of appetite occurs in meningitis patients for reasons that are yet undetermined.
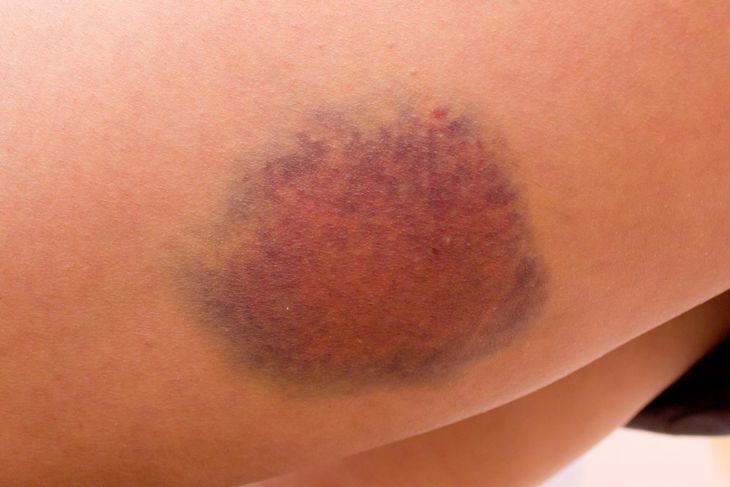
Skin Rash
In rare cases where the meningococcal bacterium is responsible for meningitis, a distinctive rash may appear upon the skin at any site on the body. It is a reddish-purple rash that resembles a bruise and does not turn white if a glass is pressed against it (as it would with other kinds of rashes). The rash could be symptomatic of blood poisoning, and thus it is advised that if such a rash is spotted on one’s body, medical assistance be sought immediately. In fact, the incidence of the rash should be treated as a medical emergency.
Seizures
People suffering from very severe meningitis may also suffer from seizures. The exact pathophysiology of their occurrence is yet unknown. However, it is suggested that the infection affects the brain in ways that may lower the seizure threshold. This may cause a patient to experience involuntary muscle spasms or even lose consciousness in extreme cases. It is not necessary that recurrent seizures occur and therefore if an individual suffers a seizure, even just a mild one, it is of utmost importance that a physician is consulted immediately.

 Home
Home Health
Health Diet & Nutrition
Diet & Nutrition Living Well
Living Well More
More