Dystonic reactions are a form of secondary or acquired dystonia, the involuntary contraction of certain muscles. These reactions can affect several different parts of the body and can result from a variety of outside influences, though they are most commonly a side-effect of medication.
Signature Signs
The main characteristic of an acute dystonic reaction is involuntary contractions of muscles, usually in the extremities, sometimes causing strange movements or postures. Common locations for a dystonic reaction are the face, neck, pelvis, abdomen, and larynx. The symptoms may occur in continuous or intermittent patterns.
Triggers
Most dystonic reactions are negative responses to medications, often antipsychotics and drugs to fight nausea and vomiting. Many of the most commonly used antipsychotics can cause dystonic reactions, but newer drugs pose a significantly lower risk. Various antihistamines, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants can also trigger dystonic reactions.
Types
Doctors recognize a few of the more common and well-defined dystonic reactions, naming them for their symptoms and location:
Buccolingual Crisis: lockjaw, fixed smile, grimacing, difficulty controlling speech muscles, difficulty swallowing
Torticollis: the head or neck is turned to one side
Tortipelvic Crisis: abdominal wall, hip, and pelvic muscle contractions
Oculogyric Crisis: spasms of the muscles around the eyes, often causing the eyes to gaze upward
Opisthotonus: painful, forced extension of the neck; the back may also extend
Pseudomacroglossia: the tongue protrudes, is not swollen but may feel swollen
Laryngospasm: uncommon; a spasm of vocal cords, causing difficulty speaking or breathing
Spasticity: trunk or limb muscles may become extremely tight due to long-term contraction
Causes and Mechanisms
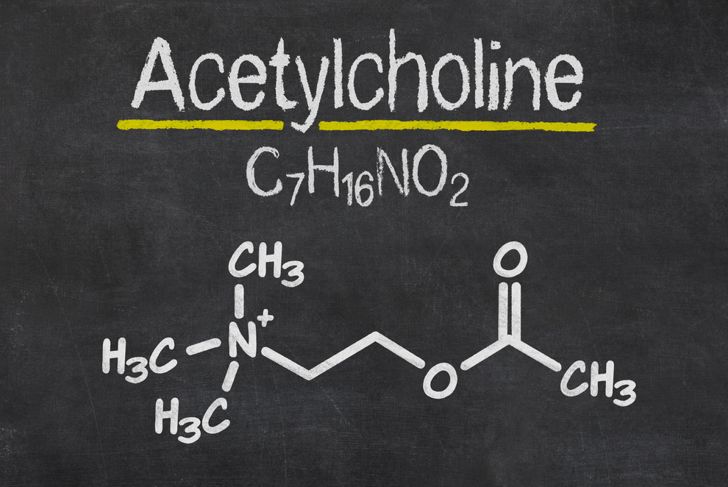
Medical researchers and other experts have yet to discover the exact causes of acute dystonic reactions. The most prominent theory involves interactions between the neurotransmitters in a specific part of the brain. Acetylcholine inhibits movement, while dopamine excites movement. Medications that block dopamine receptors, like antipsychotics, may interrupt the balance between these neurotransmitters. The result is an acute dystonic reaction.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a dystonic reaction begins similarly to diagnosing any other reaction. A doctor may begin by examining the airways and assessing circulation. They may also ask questions about the patient’s medical history and any prescribed medications. Typically, if a person’s symptoms are the result of an acute dystonic reaction, their mental status and vital signs will not change.
Symptoms Responsible for Misdiagnosis
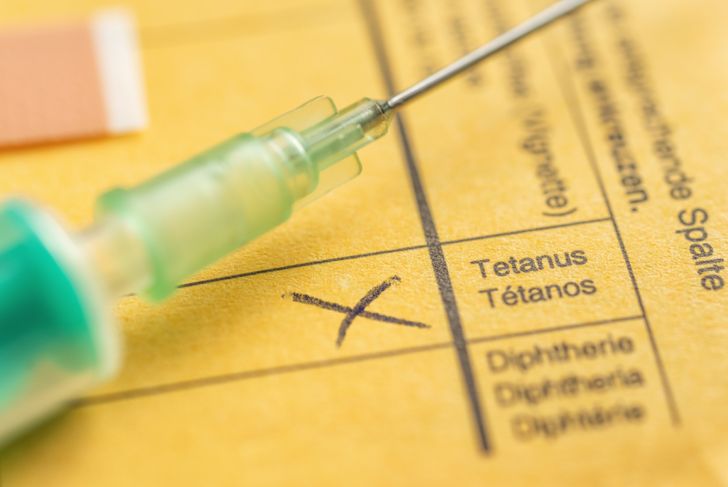
Doctors and other healthcare workers may assume several of the symptoms of dystonic reactions are signs of other conditions because dystonic reactions are quite rare. For example, jaw contractions may lead to a tetanus diagnosis. They may diagnose airway reactions as typical hyperventilation. Pseudomacroglossia may be mistaken for an allergic reaction.
Epidemiology
Currently, experts do not know the exact incidence of acute dystonic reactions, due either to actual rarity or simply a lack of awareness. One study showed a 6.8% prevalence of dystonic reactions in adults who took antipsychotics as treatment. These reactions appear to be more common in males, young adults, people with a history of dystonic reactions, and people who recently used cocaine.
Treatment
Treating dystonic reactions involves balancing the neurotransmitter issues. Medications like anticholinergics, which interrupt the actions of acetylcholine, are among the most effective treatments for dystonic reactions. Most patients respond positively to these drugs in a matter of minutes. In some cases, antihistamines may be helpful. Rarely, do anticholinergics and antihistamines also trigger a dystonic reaction. In these cases, patients require a more specific treatment approach.
Dangers of Dystonic Reactions
Dystonic reactions, while sometimes distressing, are often transient and end relatively quickly. Most people also respond very positively to treatment, meaning the reactions are rarely dangerous. However, laryngeal dystonia or laryngospasms can be life-threatening. Minor signs of laryngeal dystonia are difficulty speaking or a loss of voice. As the dystonia worsens, the muscles may obstruct the airway, making breathing impossible.
Avoiding Recurrence
Because the best predictor of an acute dystonic reaction is a history of having dystonic reactions, people should do their best to avoid exposure to the drug they already know triggers them. In some cases, this requires being in frequent contact with a physician while trying a variety of medications to find one that is effective without causing a reaction. If a person has severe symptoms, such as breathing issues, they may need to remain in a hospital for several days for observation after a dystonic reaction.

 Home
Home Health
Health Diet & Nutrition
Diet & Nutrition Living Well
Living Well More
More