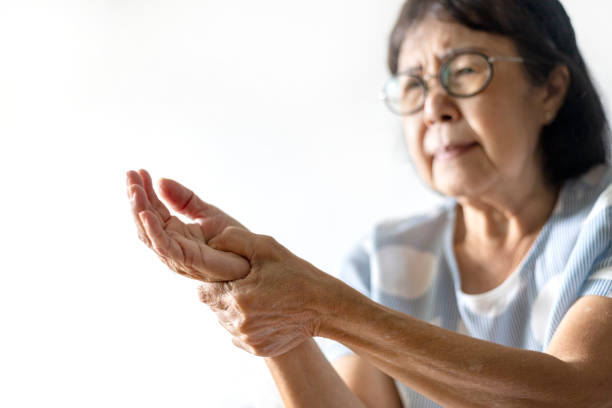
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by the compression of the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, in the narrow passageway called the carpal tunnel. The symptoms of CTS can range from mild to severe and can have a significant impact on daily life, including work and activities of daily living.
The most common symptoms of CTS include numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and fingers, particularly the thumb, index, middle and ring fingers. These symptoms often start gradually and can worsen over time if left untreated. Pain may also be present in the wrist, forearm, and shoulder, and can extend up the arm. In severe cases, the affected hand may feel weak, making it difficult to grip objects or perform fine motor tasks.
In addition to these symptoms, some people with CTS may experience clumsiness, dropping objects, and difficulty performing routine tasks such as buttoning clothes or typing. Some people may also experience sleep disturbances due to the discomfort caused by the symptoms.
The causes of CTS are not well understood, but certain factors are thought to contribute to its development. These include repetitive motions, such as typing or using a mouse for extended periods of time, as well as conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, and pregnancy, which can cause swelling in the wrist. Additionally, people who have a history of wrist injury or who have a family history of CTS may be at a higher risk for developing the condition.
Diagnosis of CTS typically begins with a physical examination and review of the patient’s medical history. The physician may also perform nerve conduction studies, which measure the speed and strength of nerve impulses, and electromyography, which measures the electrical activity of muscles, to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for CTS is aimed at reducing the pressure on the median nerve and relieving symptoms. In mild cases, non-surgical treatments such as wrist splinting, anti-inflammatory medications, and corticosteroid injections may be recommended. These treatments can help reduce swelling and relieve pressure on the median nerve.
For more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve the pressure on the median nerve. The most common surgical procedure for CTS is called a carpal tunnel release, which involves cutting the transverse carpal ligament to enlarge the carpal tunnel and reduce pressure on the median nerve. This procedure can be performed using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive endoscopic surgery, depending on the patient’s preference and medical history.
Physical therapy is often recommended after surgery to help restore strength and flexibility in the wrist and hand. This can include exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles and tendons in the wrist, as well as activities to improve fine motor skills and coordination.
In addition to these treatments, lifestyle modifications can also help alleviate the symptoms of CTS. This may include taking frequent breaks from repetitive activities, using ergonomic tools and equipment, and practicing good posture. Some people may also find relief from alternative therapies such as acupuncture or massage.
In conclusion, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by the compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel and can result in numbness, tingling, weakness, and pain in the hand and fingers. Treatment for CTS is aimed at reducing pressure on the median nerve and relieving symptoms, and can include non-surgical treatments such as wrist splinting and anti-inflammatory medications, as well as surgical procedures such as carpal tunnel release.

 Home
Home Health
Health Diet & Nutrition
Diet & Nutrition Living Well
Living Well More
More