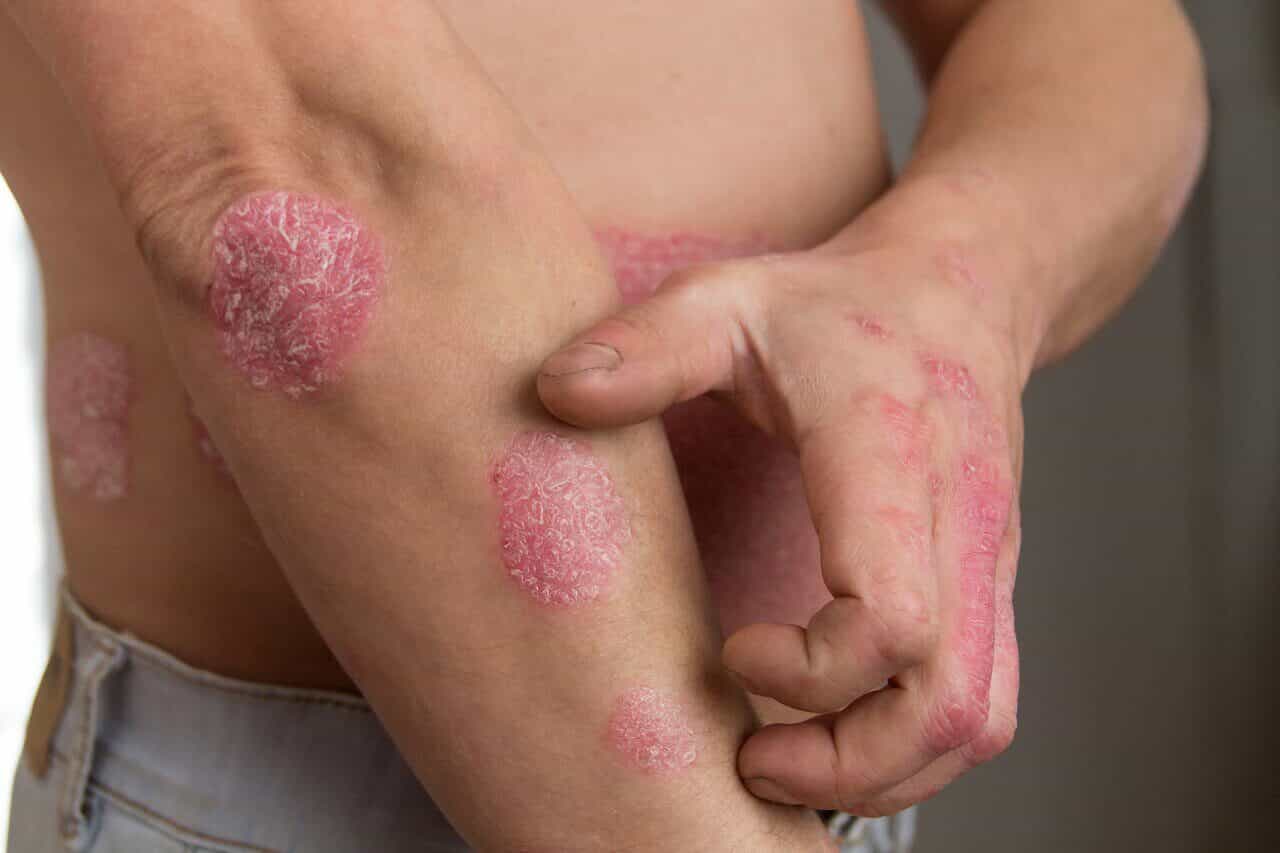
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin that can be itchy, painful, and unsightly. The symptoms of psoriasis can vary from person to person, and the severity of the condition can range from mild to severe. In this article, we will explore the different symptoms of psoriasis and the various treatment options that are available to help manage this condition.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
The first symptom of psoriasis is the appearance of red, scaly patches on the skin. These patches, known as plaques, can occur anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. The plaques can be itchy and painful, and they can also crack and bleed. In some cases, the plaques may be covered with a thick, white scale that can be difficult to remove.
Another symptom of psoriasis is joint pain and stiffness. This is known as psoriatic arthritis, and it affects up to 30% of people with psoriasis. The joint pain and stiffness can be severe and can make it difficult to perform daily tasks. In some cases, the joint pain may be accompanied by swelling and redness.
In addition to skin and joint symptoms, psoriasis can also cause other symptoms such as fatigue, depression, and anxiety. These symptoms can be caused by the physical and emotional toll of living with psoriasis. The condition can also affect a person’s self-esteem and social life, making it difficult to interact with others.
The cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the risk factors for psoriasis include a family history of the condition, smoking, obesity, and stress.
Treatment for Psoriasis
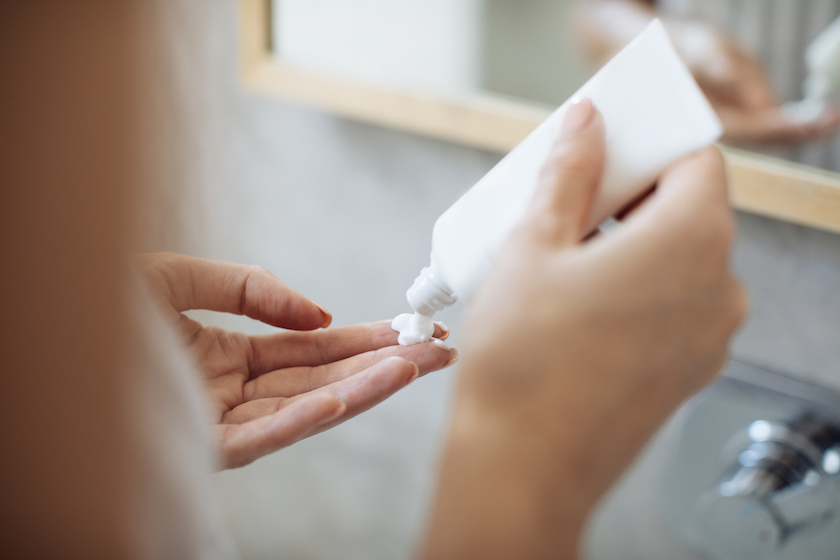
The treatment for psoriasis varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s preferences. Some of the most common treatments for psoriasis include topical creams and ointments, light therapy, and oral or injectable medications.
Topical creams and ointments are often the first line of treatment for mild to moderate psoriasis. These medications are applied directly to the affected skin and can help to reduce inflammation, itching, and scaling. Some of the most commonly used topical medications include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and retinoids.
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, is another option for treating psoriasis. This treatment involves exposing the affected skin to ultraviolet light, which can help to slow the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation. Light therapy is typically done in a doctor’s office or at home using a special light box.
Oral and injectable medications are typically reserved for more severe cases of psoriasis. These medications work by suppressing the immune system, which can help to reduce inflammation and slow the growth of skin cells. Some of the most commonly used oral and injectable medications include methotrexate, cyclosporine, and biologic drugs.
In addition to traditional medical treatments, there are also a number of alternative therapies that may be helpful for managing psoriasis. These include dietary changes, exercise, and stress management techniques. Some people find that a combination of traditional and alternative therapies works best for them.
In conclusion, psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that can cause a wide range of symptoms, including red, scaly patches, joint pain, and fatigue. The cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The treatment for psoriasis varies depending on the severity of the condition.

 Home
Home Health
Health Diet & Nutrition
Diet & Nutrition Living Well
Living Well More
More