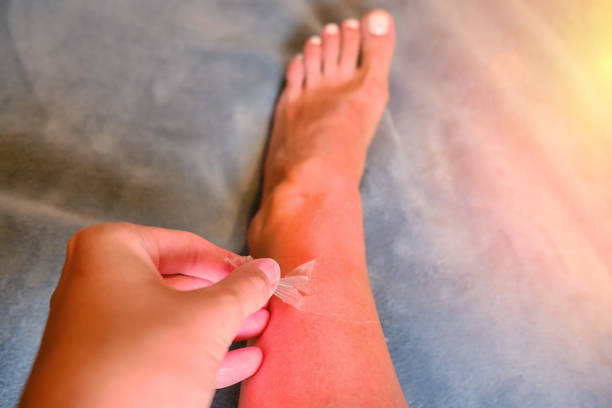
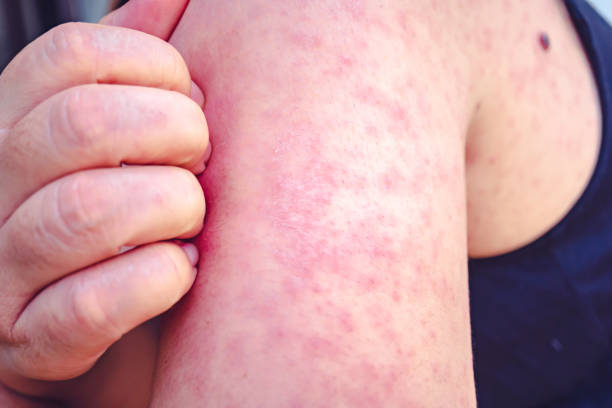
Sun poisoning rash, also known as polymorphous light eruption (PLE), is a skin reaction that occurs as a result of overexposure to the sun. It affects people of all ages, but is more common in women and fair-skinned individuals. Sun poisoning rash is not a true form of poisoning, but the term is used to describe the symptoms that occur as a result of the skin’s exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun.
Sun Poisoning Rash is a condition caused by overexposure to the sun. It results in a skin rash that can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as pain, itching, and blistering. The skin can also become red, swollen, and sensitive to the touch.
Symptoms of Sun Poisoning Rash
Sun poisoning rash symptoms can range from mild to severe and can include the following:
Itching: The most common symptom of sun poisoning rash is intense itching, which can be accompanied by a burning sensation.
Redness: The skin may become red and inflamed as a result of sun exposure, which can be accompanied by swelling.
Blistering: Sun poisoning rash may cause the skin to blister, especially in severe cases. The blisters can be small or large, and can be painful to the touch.
Hives: Sun poisoning rash can cause hives to form on the skin, which are raised, itchy welts that are usually red in color.
Peeling: Sunburned skin may start to peel, which can be accompanied by itching and discomfort.
Fatigue: Sun poisoning rash can cause fatigue, headache, and muscle aches, which are symptoms of a mild sunstroke.
Nausea: Nausea and vomiting can occur as a result of sun exposure, especially in severe cases.
Treatment for Sun Poisoning Rash
Sun poisoning rash can be treated with a combination of self-care measures and over-the-counter medications. The following are some of the most effective treatments for sun poisoning rash:
Cool compresses: Applying cool compresses to the affected area can help to soothe the skin and reduce itching and burning.
Over-the-counter pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
Hydrocortisone cream: Hydrocortisone cream can be applied to the affected area to reduce itching and redness.
Aloe vera: Aloe vera gel or cream can be applied to the skin to soothe and hydrate sunburned skin.
Antihistamines: Antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine, can help to relieve itching and hives.
Avoid sun exposure: It is important to avoid further sun exposure until the sun poisoning rash has healed, as this can make the symptoms worse.
Wear protective clothing: When going out in the sun, it is important to wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and pants, as well as a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses.
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen: Sunscreen with a high SPF should be applied to the skin before going out in the sun, and should be reapplied every two hours, or after swimming or sweating.
The best way to prevent sun poisoning rash is to take steps to protect the skin from UV radiation from the sun. The following are some tips for preventing sunburn and sun poisoning rash
Conclusion
Sun poisoning rash is a condition caused by overexposure to the sun. It results in a skin rash that can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as pain, itching, and blistering. The most common symptoms of sun poisoning rash include skin rash, nausea and vomiting, headache, dehydration, and sunburn. The most effective treatments for sun poisoning rash include over-the-counter pain relief, cold compresses, hydration, antihistamines, and topical corticosteroids. To prevent sun poisoning rash, it is important to avoid overexposure to the sun and to protect the skin with sunblock and clothing.

 Home
Home Health
Health Diet & Nutrition
Diet & Nutrition Living Well
Living Well More
More