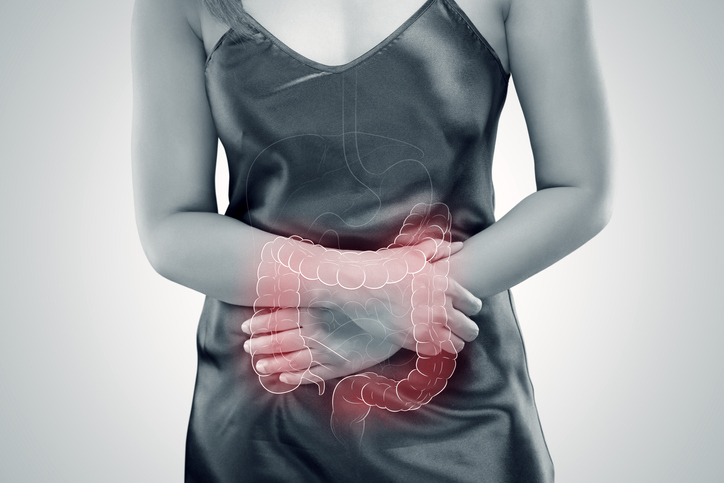
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that affects the colon and rectum. It causes inflammation, ulcers, and bleeding in the lining of the large intestine. Symptoms of UC can range from mild to severe and can include diarrhea, abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, and weight loss.
The exact cause of UC is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with a family history of IBD, as well as those who smoke, have a higher risk of developing UC.
Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
The most common symptom of UC is diarrhea, which can be accompanied by blood or mucus. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain and cramping, rectal bleeding, and the urgent need to have a bowel movement. Some people with UC may also experience weight loss, fatigue, and anemia.
Diagnosis of UC typically involves a combination of medical history, physical exam, and laboratory tests. A colonoscopy, in which a camera is inserted into the rectum to visualize the colon, is often used to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for Ulcerative Colitis
Treatment for UC depends on the severity of symptoms and the extent of inflammation. Mild to moderate cases may be treated with anti-inflammatory medications, such as 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) compounds, corticosteroids, or immunomodulators. Severe cases may require stronger medications, such as biologics or surgery.
5-ASA compounds, such as mesalamine, are the first line of treatment for mild to moderate UC. They work by reducing inflammation in the colon. Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can also be used to reduce inflammation, but they are typically reserved for more severe cases due to their potential side effects.
Immunomodulators, such as azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine, can also be used to treat UC. These medications work by suppressing the immune system and reducing inflammation. Biologics, such as infliximab and adalimumab, are a newer class of medications that target specific proteins involved in inflammation.
In severe cases of UC, surgery may be necessary to remove the diseased portion of the colon. This procedure, known as colectomy, can provide relief from symptoms and may even lead to remission of the disease.
It’s important to note that lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can also play a role in managing UC. Drinking plenty of fluids, eating a diet high in fiber, and avoiding foods that may aggravate symptoms can help to control diarrhea and inflammation.
In conclusion, Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation, ulcers, and bleeding in the lining of the large intestine. Symptoms of UC can range from mild to severe and can include diarrhea, abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, and weight loss. Treatment options include anti-inflammatory medications, immunomodulators, biologics, and surgery. Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, can also help to manage symptoms. It’s important for people with UC to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that meets their specific needs.

 Home
Home Health
Health Diet & Nutrition
Diet & Nutrition Living Well
Living Well More
More