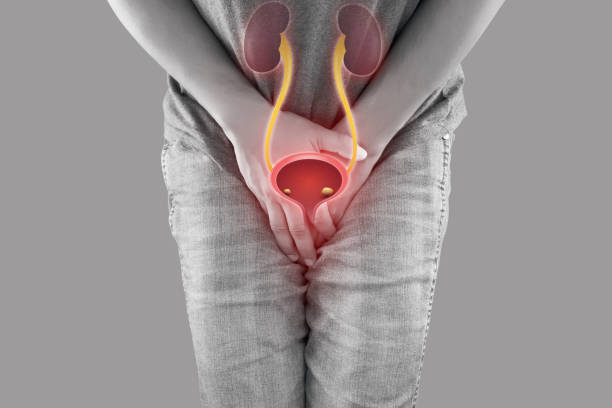
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common health issue that affects millions of people each year. UTIs are typically more prevalent in women, but men can also suffer from this type of infection. The symptoms of UTIs in men can vary, but it is important to seek prompt medical treatment if you suspect you may have a UTI.
A UTI is a bacterial infection that occurs in the urinary tract. The urinary tract is made up of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. When bacteria enter the urinary tract, it can cause an infection that leads to inflammation and pain. UTIs are more common in women than in men due to the anatomy of the female urinary tract. However, men can still develop UTIs, especially if they have certain risk factors such as an enlarged prostate, weakened immune system, or a history of bladder catheterization.
Symptoms of UTIs in Men
The following are some of the common symptoms of UTIs in men:
Painful urination: A man with a UTI may experience a burning sensation while urinating. This is because the bacteria in the urinary tract cause inflammation and irritation.
Urgency: The urge to urinate frequently and immediately is another symptom of a UTI in men.
Cloudy or bloody urine: The presence of blood or cloudy particles in the urine is a sign of a UTI. This is because the bacteria in the urinary tract can cause damage to the bladder or urethra.
Foul-smelling urine: UTIs can cause a change in the odor of the urine, making it smell foul or strong.
Lower abdominal pain: Men with UTIs may experience pain or discomfort in the lower abdominal area. This is because the bladder, which is located in the lower abdomen, is affected by the infection.
Fatigue: A man with a UTI may experience fatigue or general malaise, as the body tries to fight off the infection.
If you suspect that you may have a UTI, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Your doctor will conduct a physical examination, and may order a urine sample to test for the presence of bacteria. The results of this test will help your doctor determine the best course of treatment.
Treatment for UTIs in Men
The treatment for UTIs in men typically involves antibiotics. Antibiotics work by killing the bacteria that cause the infection. Your doctor will prescribe a specific antibiotic that is effective against the type of bacteria that is causing your UTI.
It is important to take the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if you start feeling better before you have finished the medication. This will help to ensure that all of the bacteria are eliminated, and prevent the risk of a reoccurrence of the infection.
In addition to antibiotics, there are other steps that you can take to help reduce your risk of developing UTIs. These include:
Drinking plenty of water: Drinking plenty of water will help flush bacteria out of your urinary tract, reducing the risk of UTIs.
Wiping front to back: Wiping from front to back after using the toilet will help prevent bacteria from the anus from entering the urinary tract.
Empty your bladder regularly: Regularly emptying your bladder will help flush out any bacteria that may be present in the urinary tract.
Avoiding irritants: Avoiding irritants such as bubble baths, douches, and scented products can help reduce the risk of UTIs.
Wear loose-fitting clothing: Wearing loose-fitting clothing can help reduce the risk of UTIs by allowing the skin to breathe and reducing friction in the genital area.
It is important to take the antibiotics as directed by your doctor and to finish the entire course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better before the antibiotics are finished. Stopping the antibiotics too soon can lead to a recurrence of the infection and can also lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Conclusion
UTIs are a common health issue that can affect men. The symptoms of UTIs in men include painful urination, urgency, cloudy or bloody urine, foul-smelling urine, lower abdominal pain, and fatigue. If you suspect that you may have a UTI, it is important to seek prompt medical attention. Treatment typically involves antibiotics, and there are also steps that you can take to reduce your risk of developing UTIs.

 Home
Home Health
Health Diet & Nutrition
Diet & Nutrition Living Well
Living Well More
More