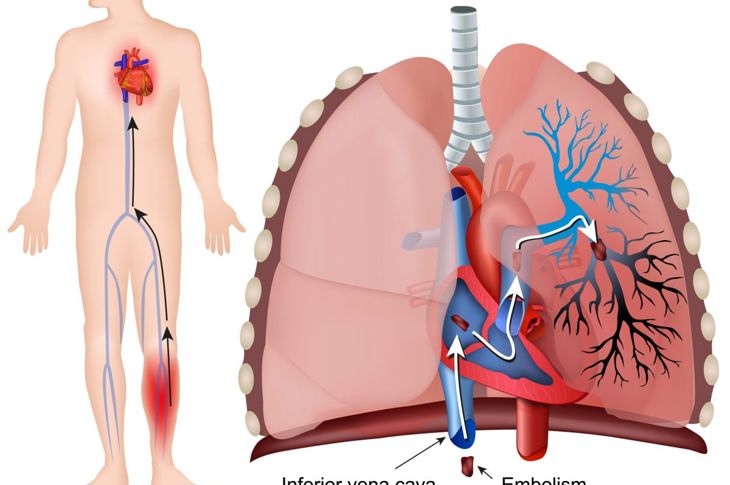
A thrombus occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein and stays there. If the clot detaches from the wall and travels to another part of the body, it becomes an embolus. A pulmonary embolus is a clot that traveled from elsewhere in the body and is now blocking an artery in the lung. Pulmonary embolism is a serious medical condition that can be life-threatening, especially if the clot is large or if there is more than one blockage.
Common Symptoms
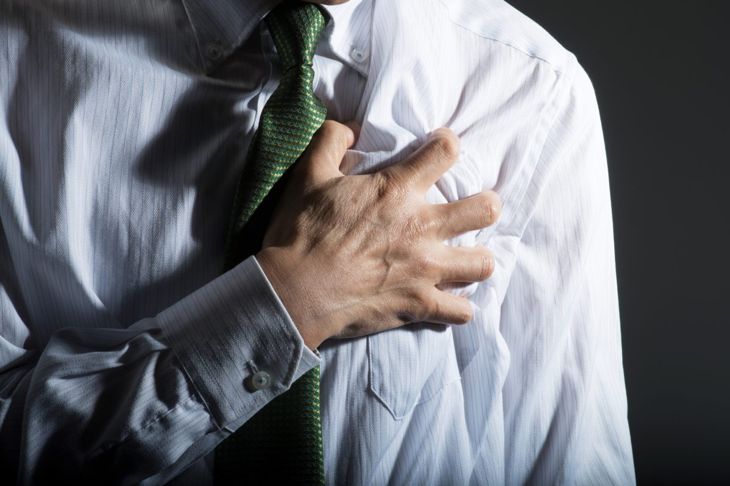
Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism vary depending on the size of the clot, how much lung tissue is affected, and whether the individual has other heart or lung conditions. Signs include sudden shortness of breath that worsens with exertion, significant chest pain, and a cough that may produce blood-tinged secretions. That said, half of all people with a pulmonary embolism have no symptoms at all.
Additional Symptoms
Other symptoms may occur depending on the severity of the pulmonary embolism. A person may experience clammy or discolored skin, fever, sweating, lightheadedness, or rapid or irregular heart rate. Pain or swelling in one or both calves may also develop, possibly indicating deep vein thrombosis, which could be the source of the initial clot.
Causes
The most common cause of pulmonary embolism is deep vein thrombosis. As mentioned, these clots form in the calves and break free, traveling to the lungs. In many cases, a pulmonary embolism is caused by more than one clot blocking the artery. Occasionally, blockages stem from problems other than blood clots, such as air bubbles, a fragment of a tumor, or fat from broken long bones. When lung tissue death occurs as a result of any type of blockage, it is referred to as a pulmonary infarction.
Medical Conditions and Risk Factors
Some medical conditions put people at higher risk for clots and pulmonary embolism, including heart disease, some cancers and chemotherapy treatments, and surgery. The latter is one of the leading causes of blood clots, which is why hospitals take measures to prevent them from forming, both before and after surgery. People with a family history of blood clots or pulmonary embolus are also at higher risk.
Other Risk Factors
Blood clots leading to pulmonary embolism are more likely to form during periods of inactivity — extended bed rest after surgery or injury and long trips sitting in a car or plane, to name a few. Being overweight, smoking, pregnancy, birth control, and supplemental estrogen also increase the risk of blood clots.
Diagnosis
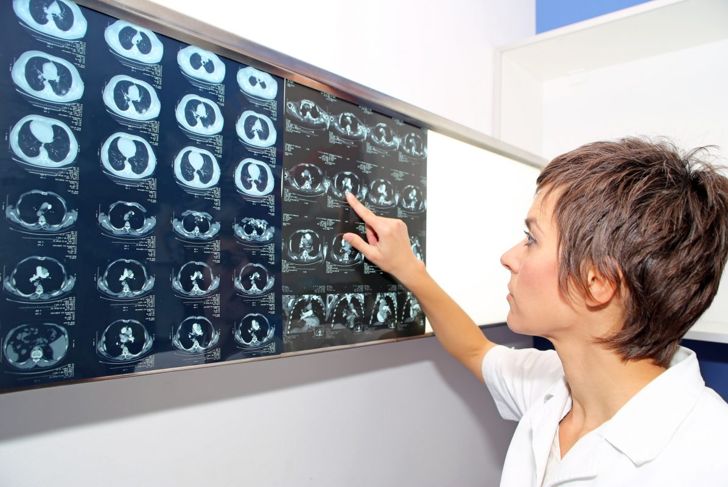
Pulmonary embolus is not always easy to diagnose, especially if there are no symptoms or if other heart or lung problems are present. Diagnostic testing includes CT scans and MRIs, angiograms to check blood flow, and ultrasounds of the leg to assess for clots. The doctor may do blood tests to measure the amount of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the blood and to check clotting factors.
Treatment
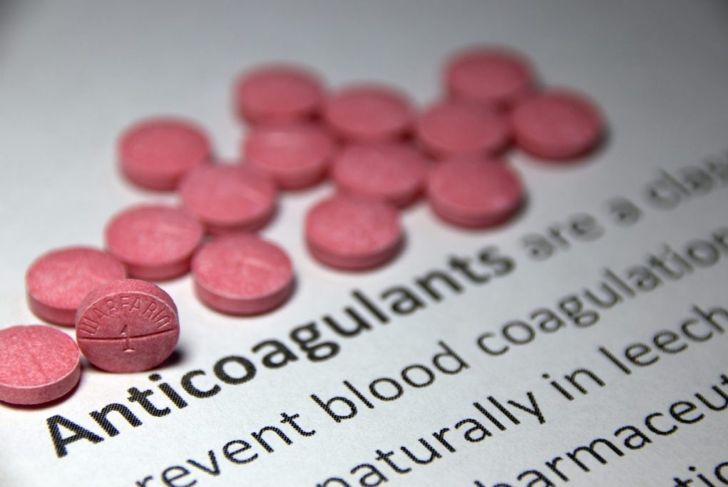
Treatment for pulmonary embolism typically requires hospitalization and close observation. In most cases, physicians administer blood thinners to prevent future clots. In an emergency situation, thrombolytic therapy can dissolve any clots that have already formed. Blood tests determine clotting times and can help determine the necessary interventions.
Other Interventions
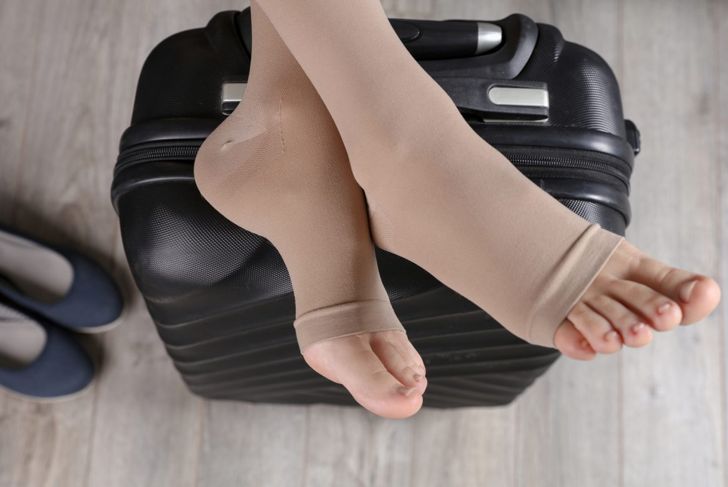
Medical professionals often recommend compression stockings or support hoses to prevent deep vein thrombosis. These special socks compress the calf to help prevent blood pooling in the lower extremities. In some cases, people may require surgery to remove the embolus from the pulmonary artery, or the surgeon may place a filter to prevent clots from entering the lungs. These interventions do not stop future clots from forming, however.
Complications
Pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening, especially when undiagnosed and untreated, and in these cases, about a third of people do not survive. With prompt treatment, however, the survival rate increases dramatically. A pulmonary embolus can also lead to pulmonary hypertension if the arteries are obstructed and the heart has to work harder to circulate blood through the lungs. This eventually damages the heart because it has to work much harder.
Prevention
The main way to prevent pulmonary embolus is to prevent clots, particularly deep vein thrombosis. This is why hospitals take great care to do everything they can to prevent clots from forming while patients are under their care. These measures include blood thinners, compression stockings, and elevating the legs of bedbound individuals. Developing a blood clot while traveling is rare, but people with risk factors should stay hydrated and take hourly breaks from sitting.

 Home
Home Health
Health Diet & Nutrition
Diet & Nutrition Living Well
Living Well More
More