Blue light is a prime example of how harmful too much of a good thing can be. Our bodies need the blue light sunlight naturally radiates. However, after the sun sets, artificial lights continue to illuminate our homes and computer screens, and constant exposure to blue light is producing dark consequences for our health. Electricity and technology extend waking hours to around the clock. Studies show blue light from electronic devices is affecting vision, sleep, and mental health and continue to expose its dangers.
1. What is Blue Light?
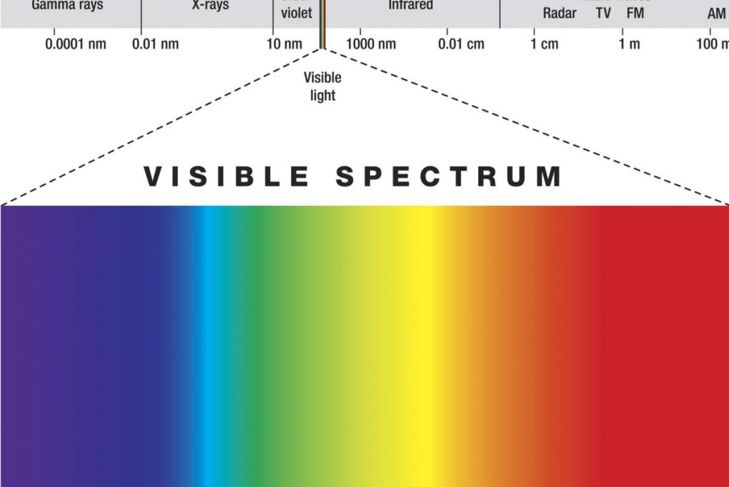
Sunlight or white light contains red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet light, as well as infinite shades of each. Every color has a unique wavelength and energy or electromagnetic radiation. Light rays on the red end of the visible light spectrum have longer wavelengths and emanate less energy. On the opposite end, blue light rays have shorter wavelengths and radiate more energy. When the light rays on the blue end of the light spectrum bounce on water and air molecules in the atmosphere, they scatter more easily than other light rays with longer wavelengths. This is why we see a cloudless sky as blue. About one-third of all visible light is blue light.
Sources of Blue Light
Sunlight is by far the largest source of blue light. Other sources include:
- LED light
- Fluorescent light
- CFL bulbs
- Computer, smartphone, and tablet screens
Blue light exposure from man-made devices is minute compared to what emanates from the sun. However, eye care professionals are concerned about the long-term impact of these artificial sources due to their proximity to our eyes and the sometimes excessive amount of exposure.
Effect on Sleep
The American Optometric Association asserts that blue light has a significant impact on wakefulness and alertness. Blue light stimulates certain photosensitive cells within the retina that influence the circadian rhythm. This stimulation is beneficial to promote alertness in the daytime, but it inhibits the onset of sleep at bedtime. As daylight wanes, the pineal gland releases melatonin, the sleep hormone. However, high-energy blue light inhibits melatonin production, thereby diminishing sleep quantity and quality. Sleep deprivation is increasing along with the use of electronic devices, wreaking havoc on many bodies and minds.
Mental Health and Blue Light
The circadian system is integral to vital physiological functions beyond the sleep-wake cycle. It is responsible for behavioral processes that affect mood. One of the dangers of blue light is how it confuses the circadian clock, with troubling results. Translational Psychiatry posits that sleep disturbance contributes to the onset and progression of mood disorders. Scientists are now investigating a suspected correlation between circadian rhythm imbalance and mental illnesses.
Digital Eye Strain
Digital eye strain (DES), which experts refer to as computer vision syndrome or vision fatigue, affects at least half of computer users. Symptoms include those related to accommodative vision stress and dry eye. Since blue light scatters so easily, it reduces contrast and makes focusing more difficult. Thus, prolonged exposure can lead to DES.
Cancer Concerns
Research has yet to agree on any direct correlation between blue light and cancer. However, the light’s effect on melatonin production is a suspected contributing factor. Melatonin not only promotes sleep but also protects against cancer. Preliminary research suggests that the suppression of this hormone may increase cancer risk.
Blue Light and Children
A 2016 European Early Childhood Education Research Journal study found that nearly seven out of ten children use a computer regularly. Their little eyes are more sensitive to blue light than those of adults, and research has yet to determine the long-term effects of blue light exposure starting at such young ages. However, a 2019 study in BMC Public Health garnered considerable evidence connecting longer screen time to shorter sleep time among children seven to 24 months.
Obesity
Research in the Annals of Medicine suggests that sleep deficiency, circadian disruption, and melatonin suppression are contributing to the growing obesity epidemic around the world. As blue light encourages wakefulness, people exposed to it at night tend to be hungrier. When their bodies should be resting and repairing cells, they are instead consuming calories, but not creating as much insulin as during the day. Carbohydrates from these late-night foods build up in the blood or are stored as fat.
How Diet Can Help
What we eat can contribute significantly to eye health. It is important to consume foods rich in nutrients that strengthen the eyes and reduce inflammation. Research notes eye-enhancing benefits from eating foods high in omega-3 fats, vitamin C, lutein, and zeaxanthin. According to a 2014 study published in BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, polyphenols in bilberries and lingonberries guarded against retinal damage from blue light.
Prevention
The best way to avoid the dangers of blue light is to reduce or eliminate exposure at night. Since this is not always feasible or desirable, these steps can also protect vision and physical and mental health:
- Avoid bright screens two to three hours before bedtime.
- Wear blue-light-blocking glasses with a yellow, amber, red, or orange lens.
- Install an app that filters blue/green light.
- Get out in the sunshine during the day to promote better sleep at night.
- Choose dim red or amber night lights as they have the least impact on melatonin production and circadian rhythm.
- Practice eye exercises such as 20-20-20: at least every 20 minutes, look away from the blue light source toward something at least 20 feet away for 20 seconds.

 Home
Home Health
Health Diet & Nutrition
Diet & Nutrition Living Well
Living Well More
More