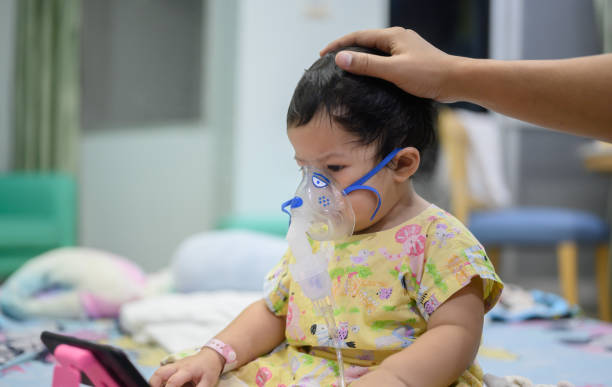
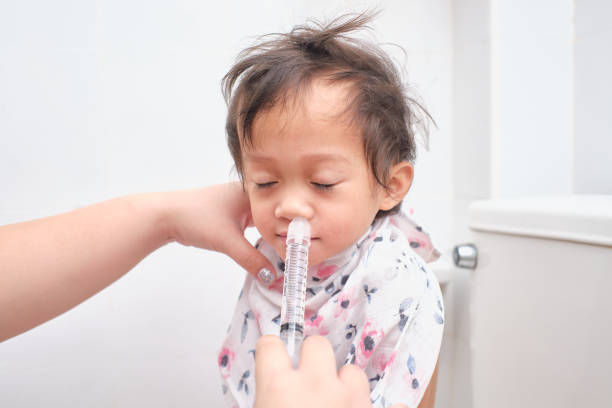
RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) is a common respiratory virus that affects infants and young children. The symptoms of RSV in infants include:
Coughing and wheezing
Rapid or difficult breathing
Bluish color of the skin, lips, or nails
High fever
Reduced appetite and activity
Nasal congestion and runny nose
Body aches and fatigue
In severe cases, RSV can cause pneumonia or bronchiolitis, which can be life-threatening for infants. RSV is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes.
The treatment for RSV in infants mainly focuses on relieving the symptoms and supporting the infant’s breathing. This may include:
Providing plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration
Humidifying the air to relieve nasal congestion
Elevating the head of the infant’s bed to ease breathing
Giving over-the-counter medication, such as acetaminophen, to reduce fever and body aches
Administering oxygen, if necessary, to support breathing
Prescribing antiviral medication or antibiotics, if a secondary infection is present
In severe cases, infants with RSV may require hospitalization for close monitoring and treatment, such as supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation.
It is important for parents to be vigilant for the symptoms of RSV in their infants and seek medical attention if they suspect their child has the virus. To prevent the spread of RSV, it is essential to practice good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and keeping the infected child isolated.
In conclusion, RSV is a common respiratory virus that affects infants and young children. The symptoms of RSV in infants include coughing and wheezing, rapid or difficult breathing, and high fever, among others. The treatment for RSV in infants mainly focuses on relieving the symptoms and supporting the infant’s breathing, and in severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary. Parents should be vigilant for the symptoms of RSV in their infants and practice good hygiene to prevent its spread.

 Home
Home Health
Health Diet & Nutrition
Diet & Nutrition Living Well
Living Well More
More